66 questions match your search.
The test dose of local anesthetic administered through an epidural needle or catheter should be sufficient to produce
- (A) bradycardia
- (B) seizure activity
- (C) hypotension
- (D) segmental analgesia
- (E) spinal anesthesia
Which of the following statements concerning diabetes mellitus in pregnancy is true?
- (A) Beta-mimetic tocolytics cause maternal hypoglycemia
- (B) Epidural anesthesia produces hyperglycemia
- (C) Fetal insulin secretion is suppressed
- (D) Maternal insulin does not cross the placenta
- (E) Maternal insulin resistance develops abruptly after delivery
At term which of the following would produce the greatest increase in uterine blood flow?
- (A) Increasing PaO2 to greater than 100 mmHg
- (B) Administering ritodrine intravenously
- (C) Administering halothane to 1 MAC
- (D) Administering magnesium sulfate intravenously
- (E) Increasing PaCO2 from 35 to 40 mmHg
At the time of cesarean delivery, thick dark meconium is noted and the newborn is flaccid, apneic, bradycardic, and cyanotic. The most appropriate initial action is
- (A) atropine administration
- (B) sodium bicarbonate administration
- (C) naloxone administration
- (D) controlled ventilation
- (E) tracheal suctioning
To eliminate involuntary expulsive effort with contraction in the second stage of labor, a nerve block must include at least
- (A) T6-T12
- (B) T4-S5
- (C) T8-L2
- (D) L1-S2
- (E) S2-S4
Which of the following is a manifestation of preeclampsia?
- (A) Hypovolemia
- (B) Increased colloid osmotic pressure
- (C) Natriuresis
- (D) Resistance to catecholamines
- (E) Thrombocytosis
A 25-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital in the early stages of labor at term. Initial hematocrit is 33%. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the hematocrit value?
- (A) Decreased erythropoietin activity
- (B) Destruction of erythrocytes by the placenta
- (C) Early placental abruption
- (D) Increased plasma volume
- (E) Iron deficiency
A multigravid woman is receiving oxytocin by infusion for augmentation of labor. Fetal heart rate is 190 bpm with beat-to-beat variability of 6 to 8 bpm. The most appropriate immediate action would be to
- (A) continue observation
- (B) sample fetal scalp blood
- (C) discontinue oxytocics
- (D) administer a beta-adrenergic blocker to the mother
- (E) deliver the fetus
In the majority of cases, fetal heart rate decelerations in a variable pattern are associated with
- (A) decreased uteroplacental perfusion
- (B) fetal head compression during contractions
- (C) umbilical cord compression
- (D) low Apgar scores at birth
- (E) low neurobehavioral scores eight hours post partum
Uterine blood flow is
- (A) autoregulated in normal unanesthetized parturients
- (B) decreased by the addition of epinephrine 1:200,000 to lidocaine administered epidurally
- (C) decreased by intravenous infusion of ritodrine in unanesthetized parturients
- (D) increased by administration of magnesium sulfate to patients with preeclampsia
- (E) unchanged after paracervical injection of lidocaine without epinephrine
Which of the following changes in pulmonary function best explains the more rapid rate of rise of alveolar concentration of volatile anesthetics in pregnant women than in nonpregnant women?
- (A) Decreased functional residual capacity
- (B) Decreased dead space ventilation
- (C) Increased cardiac output
- (D) Increased oxygen consumption
- (E) Increased pulmonary venous admixture
Each of the following factors decreases uterine blood flow EXCEPT
- (A) aortocaval compression
- (B) hypocarbia
- (C) hypoxia
- (D) sympathetic block
- (E) uterine contractions
Fetal distress is noted after administration of an epidural local anesthetic during labor. Fetal scalp pH is 7.0. Compared with a fetus with a scalp pH of 7.3, in this fetus the local anesthetic is present in
- (A) a higher concentration, with a larger fraction in the ionized form
- (B) a higher concentration, with a larger fraction in the unionized form
- (C) the same concentration, with a larger fraction in the ionized form
- (D) the same concentration, with a larger fraction in the unionized form
- (E) a lower concentration, with a larger fraction in the ionized form
A parturient receives ketamine 2 mg/kg and succinylcholine 1.5 mg/kg for induction prior to elective cesarean delivery. Which of the following is most likely to be present in the newborn infant?
- (A) Normal muscle tone
- (B) Bradycardia
- (C) Opisthotonos
- (D) Respiratory depression
- (E) Seizures
The low fetal/maternal plasma ratio of bupivacaine compared with lidocaine is due to
- (A) fetal tissue binding
- (B) fetal plasma protein binding
- (C) maternal plasma protein binding
- (D) ionization in maternal blood
- (E) ionization in fetal blood
Administration of succinylcholine 1 mg/kg to a pregnant woman rarely causes fetal neuromuscular blockade. Which characteristic of succinylcholine best explains this phenomenon?
- (A) High protein binding
- (B) Ionization
- (C) Lack of passive placental diffusion
- (D) Lipid solubility
- (E) Metabolism in the fetal liver
A 30-year-old primiparous woman delivered a healthy infant by cesarean section during uneventful spinal anesthesia with tetracaine 10 mg in 2 ml of 5% dextrose solution. Twelve hours after delivery she has bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensibility, but not touch, below T8 and paralysis of both legs. The most likely cause of this complication is
- (A) chemical arachnoiditis
- (B) injection of tetracaine into the spinal cord
- (C) demyelination of the posterior tracts
- (D) thrombosis of the anterior spinal artery
- (E) cord transection from spondylolisthesis
Following maternal epidural injection, fetal exposure to chloroprocaine is lower than fetal exposure to bupivacaine for which of the following reasons?
- (A) Chloroprocaine is metabolized by plasma cholinesterase
- (B) Chloroprocaine is more protein bound
- (C) Chloroprocaine is not readily absorbed from the epidural space
- (D) The ionized fraction of chloroprocaine in the fetal circulation is smaller
- (E) The pKa of chloroprocaine is less than that of bupivacaine
A multiparous 24-year-old woman sustains an amniotic fluid embolism during general anesthesia. The LEAST likely clinical finding is
- (A) increased end-tidal carbon dioxide tension
- (B) increased uterine bleeding
- (C) jugular venous distention
- (D) ST and T wave abnormalities on ECG
- (E) wheezing
Which of the following statements concerning the use of epidural opioids during labor is true?
- (A) Fentanyl decreases the concentration of epidural bupivacaine required for satisfactory analgesia
- (B) Fentanyl is an effective analgesic for the second stage of labor
- (C) Sufentanil is an unsatisfactory analgesic for labor
- (D) The addition of epinephrine to morphine prolongs the duration of analgesia
- (E) The duration of analgesia with fentanyl is six to ten hours
A woman is in labor at 40 weeks' gestation and the fetus is in breech presentation. Which of the following will provide adequate uterine relaxation for vaginal delivery?
- (A) Spinal anesthesia
- (B) Epidural anesthesia
- (C) Halothane anesthesia
- (D) Pudendal nerve block
- (E) Magnesium sulfate
Recognized side effects of magnesium sulfate used for the treatment of preeclampsia that would be of anesthetic concern include each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) maternal pulmonary edema
- (B) neonatal hypotonia
- (C) increased maternal sensitivity to succinylcholine
- (D) increased maternal sensitivity to vecuronium
- (E) maternal hypokalemia
A woman at 39 weeks' gestation has been in labor for 12 hours. She has had nausea and vomiting for the past eight hours. Maternal arterial blood gas values are PaO1 85 mmHg, PaCO2 31 mmHg, and pH 7.50. Which of the following is the most likely cause of fetal distress occurring at this time?
- (A) Hypocarbia-induced placental ischemia
- (B) Impaired fetal oxyhemoglobin dissociation
- (C) Shift to the left of the maternal oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve
- (D) Maternal hypovolemia
- (E) Maternal hypoxemia
The fetal heart rate and uterine contraction tracings shown are most consistent with
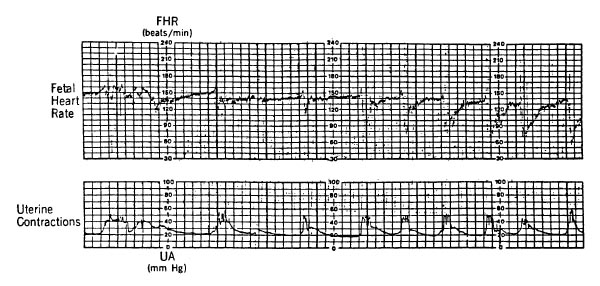
- (A) fetal acidosis
- (B) fetal cerebral hemorrhage
- (C) fetal head compression
- (D) fetal hypoxia
- (E) uteroplacental insufficiency
Numbness and tingling on the lateral aspect of the thigh 24 hours after uneventful vaginal delivery is most likely a complication of
- (A) forceps delivery
- (B) lithotomy position
- (C) pudendal nerve block
- (D) lumbar epidural anesthesia
- (E) spinal anesthesia
A woman has weakness of the right quadriceps and a decreased knee jerk reflex on the right one day after forceps delivery under epidural anesthesia. The most likely cause is
- (A) epidural hematoma
- (B) intrapelvic nerve trauma
- (C) lithotomy positioning
- (D) reaction to the preservative in the anesthetic solution
- (E) trauma from the epidural needle
A 19-year-old woman receives a spinal anesthetic for a repeat cesarean delivery. Two days later she is afebrile but has severe occipital pain that is aggravated by sitting or standing and relieved by lying flat. Associated findings would likely include
- (A) bradycardia
- (B) difficulty swallowing
- (C) diplopia
- (D) facial pain
- (E) Horner's syndrome
Which of the following drugs is LEAST likely to cross the placenta?
- (A) Lidocaine
- (B) Meperidine
- (C) Midazolam
- (D) Thiopental
- (E) Vecuronium
During active labor, 10 ml of bupivacaine 0.5% with epinephrine 1:200,000 is administered epidurally. Fifteen minutes later, maternal blood pressure is 70/50 mmHg and heart rate is 70 bpm; fetal heart rate is 90 bpm for 45 seconds, with loss of beat-to-beat variability. The most likely explanation for the fetal vital signs is
- (A) fetal bupivacaine cardiotoxicity
- (B) maternal bupivacaine cardiotoxicity
- (C) maternal hypotension
- (D) uterine artery vasoconstriction
- (E) umbilical cord compression
Postdural puncture headache occurs most commonly in which of the following patients?
- (A) Children
- (B) Elderly persons
- (C) Misn
- (D) Parturients
- (E) Persons with obesity
A parturient received 1000 ml of dextrose 5% in lactated Ringer's solution 20 minutes prior to delivery. Ten minutes later her blood glucose concentration is 580 mg/dl. In this situation
- (A) the risk for fetal intraventricular hemorrhage is increased
- (B) the risk for neonatal hypoglycemia is increased
- (C) placental glucose transport is insulin dependent
- (D) the neonate should be given dextrose 50% in water if depressed at delivery
- (E) the mother should be given insulin prior to delivery
A 25-year-old woman is undergoing emergency appendectomy at 36 weeks' gestation. Following subarachnoid injection of hyperbaric bupivacaine and placement in the supine position, the patient has nausea; heart rate is 105 bpm and blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg. Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
- (A) Displacement of the uterus to the left
- (B) Immediate tracheal intubation
- (C) Intramuscular administration of ephedrine
- (D) Placement of the operating table in the reverse Trendelenburg position
- (E) Ventilation by mask with 100% oxygen
In patients with pregnancy-induced hypertension, magnesium sulfate is most likely to
- (A) decrease maternal heart rate
- (B) decrease sensitivity to relaxants
- (C) decrease succinylcholine-induced fasciculations
- (D) prevent hypokalemia
- (E) produce fetal bradycardia
Which of the following factors is the LEAST important determinant of postdural puncture headache?
- (A) Age of the patient
- (B) Gauge of the spinal needle
- (C) Gender of the patient
- (D) Pregnancy
- (E) Time until ambulation
Which of the following drugs administered to a parturient eliminates fetal heart rate variability?
- (A) Atropine
- (B) Ephedrine
- (C) Hydralazine
- (D) Magnesium sulfate
- (E) Terbutaline
A 26-year-old woman has headache, nausea, and photophobia 36 hours after cesarean delivery for chorioamnionitis using subarachnoid block. Temperature is 38.8°C and leukocyte count is 14,200/mm3. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- (A) Oral ibuprofen
- (B) Intravenous caffeine sodium benzoate
- (C) Intravenous hydration
- (D) Epidural blood patch
- (E) Diagnostic lumbar puncture
Prilocaine is NOT recommended for obstetric regional anesthesia because it
- (A) causes fetal methemoglobinemia
- (B) has a very short duration of action
- (C) is not metabolized by the newborn
- (D) is the most toxic of the amide local anesthetics
- (E) produces a longer motor block than sensory block
The concentration of bupivacaine is higher in maternal blood than in fetal blood because
- (A) bupivacaine is metabolized in the placenta
- (B) maternal blood has a higher pH
- (C) maternal blood has greater plasma protein binding
- (D) maternal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for bupivacaine
- (E) placental transfer of bupivacaine is limited
Which of the following would be most likely to result in neonatal depression when administered to a healthy parturient during an uncomplicated labor and vaginal delivery?
- (A) Nitrous oxide 60% in oxygen supplemented with halothane 0.5% for 10 minutes before delivery
- (B) Ketamine 20 mg intravenously 30 minutes before delivery
- (C) Meperidine 100 mg intramuscularly 2 hours before delivery
- (D) Thiopental 100 mg intravenously 30 minutes before delivery
- (E) Nitrous oxide 60% in oxygen supplemented with enflurane 0.7% for 10 minutes before delivery
A 30-year-old woman underwent emergency cesarean delivery under general anesthesia at 36 weeks' gestation because of preeclampsia. Two hours after the operation, she is still intubated and apneic and cannot be aroused. Deep tendon reflexes are 1+. With mechanical ventilation at an FiO2 of 0.4, PaO2 is 130 mmHg, PaCO2 is 32 mmHg, pH is 7.45, and base excess is -0.6. The most likely cause is
- (A) hypovolemic shock
- (B) intracerebral hemorrhage
- (C) nitroprusside toxicity
- (D) overdose of magnesium sulfate
- (E) pituitary necrosis
Which of the following is most likely to decrease uterine tone?
- (A) Administration of isoflurane 1%
- (B) Administration of nitrous oxide 50%
- (C) Intravascular injection of 5 ml of 0.5% bupivacaine
- (D) Intravenous administration of ketamine 2 mg/kg
- (E) Paracervical block with 20 ml of 1% lidocaine
When PaO2 is increased to 300 mmHg in a healthy parturient at term, the umbilical vein PCs will
- (A) not change
- (B) increase slightly
- (C) decrease slightly
- (D) nearly triple
- (E) approach maternal PaO,
Which of the following statements regarding fetal heart rate patterns is true?
- (A) Early decelerations suggest umbilical cord compression
- (B) Fetal heart rates between 160 and 180 bpm are normal
- (C) Fetal heart rate unaffected by uterine contraction suggests fetal well-being
- (D) Late decelerations indicate inadequate uteroplacental perfusion
- (E) Variable decelerations indicate need for urgent delivery
Arterial oxyhemoglobin desaturation develops more rapidly following apnea in a pregnant patient at term than in a nonpregnant patient with a large intra-abdominal tumor. Which of the following findings in pregnancy is the most likely cause?
- (A) Higher cardiac output
- (B) Higher oxygen consumption
- (C) Larger anatomic dead space
- (D) Smaller blood volume
- (E) Smaller functional residual capacity
In pregnant patients, which of the following is an effect of the long-term use of cocaine?
- (A) Decreased uterine tone
- (B) Decreased thiopental requirement
- (C) Increased isoflurane MAC
- (D) Increased sensitivity to ephedrine
- (E) Lower than expected level of block with tetracaine spinal analgesia
Inhibition of labor by terbutaline causes each of the following maternal side effects EXCEPT
- (A) hyperkalemia
- (B) hypotension
- (C) ventricular dysrhythmias
- (D) hyperglycemia
- (E) pulmonary edema
Administration of magnesium sulfate for treatment of preeclampsia results in a decreased dose requirement for each of the following drugs EXCEPT
- (A) bupivacaine
- (B) halothane
- (C) midazolam
- (D) succinylcholine
- (E) vecuronium
The supine hypotensive syndrome of pregnancy
- (A) begins at 32 weeks' gestation
- (B) causes fetal distress by aortocaval compression
- (C) is corrected by Trendelenburg's position
- (D) is less likely following subarachnoid block than epidural block
- (E) occurs in 90% of supine women at 38 to 40 weeks' gestation
Gravid uterine blood flow is
- (A) autoregulated
- (B) decreased by normotensive epidural analgesia
- (C) decreased by uterine contractions
- (D) increased with an increase in maternal Pa02
- (E) unaffected by alpha-adrenergic agonists
A woman is undergoing a repeat cesarean delivery at term following a normal pregnancy. Anesthesia consists of thiopental 250 mg, succinylcholine infusion (180 mg in 20 minutes), nitrous oxide and oxygen (7:3 L/min) until delivery. Twenty minutes after the incision a floppy newborn with a 1-minute Apgar score of 5 is delivered. The most likely explanation for the infant's condition is
- (A) high serum thiopental concentration
- (B) high serum succinylcholine concentration
- (C) high serum nitrous oxide concentration
- (D) high serum glucose concentration
- (E) uterine hypoperfusion
Each of the following is an adverse effect of ritodrine used for suppression of labor EXCEPT
- (A) dysrhythmias
- (B) hyperglycemia
- (C) hyperkalemia
- (D) hypotension
- (E) pulmonary edema
Which of the following is most likely to result in oxygen desaturation in a patient with Eisenmenger's syndrome who is scheduled for cesarean delivery?
- (A) Breathing room air
- (B) Epidural administration of lidocaine
- (C) Intravenous administration of ketamine
- (D) Intravenous administration of ephedrine
- (E) Mild hypocarbia
Which of the following statements concerning the management of diabetes mellitus during pregnancy is true?
- (A) Insulin requirements remain essentially unchanged during pregnancy
- (B) Maternal blood glucose concentration of 200 mg/dL is optimal
- (C) Maternal hyperglycemia may cause neonatal acidosis
- (D) Neonatal hyperglycemia is common
- (E) Infants delivered under general anesthesia have lower Apgar scores than those delivered under spinal anesthesia
Maternal hyperventilation to a PaCO2 of 20 mmHg during labor can result in
- (A) decreased fetal trapping of local anesthetics
- (B) fetal metabolic acidosis
- (C) fetal respiratory acidosis
- (D) increased oxygen release at the placenta
- (E) uterine vasodilation
Following delivery with pudendal block, a patient requires anesthesia for removal of a retained placenta. The most appropriate anesthetic is
- (A) epidural block
- (B) ketamine analgesia with midazolam for amnesia
- (C) opioid-based general endotracheal anesthetic
- (D) potent inhaled general endotracheal anesthetic
- (E) subarachnoid block
An asymptomatic 38-year-old woman is scheduled for elective cesarean delivery. The preoperative EKG shows left axis deviation that was not present one year ago. The most appropriate next step is to
- (A) postpone the procedure and consult a cardiologist
- (B) postpone the procedure and obtain an echocardiogram
- (C) proceed with the procedure after administration of digitalis
- (D) proceed with the procedure but avoid inhalational agents
- (E) proceed without intervention since this is a normal finding
Which of the following anesthetic techniques is most appropriate for a woman in the second stage of labor?
- (A) Epidural opioids
- (B) Local infiltration of the perineum
- (C) Lumbar sympathetic block
- (D) Paracervical nerve block
- (E) Pudendal nerve block
The most likely cause of a fetal heart rate pattern of variable decelerations to 90 bpm is
- (A) aortocaval compression
- (B) compression of the fetal head
- (C) fetal acidosis
- (D) maternal hypotension
- (E) umbilical cord compression
A 28-year-old woman receives a lumbar epidural anesthetic for uncomplicated labor and delivery. During removal of the catheter, 1 cm breaks off and remains in her back. After informing the patient, the most appropriate management is
- (A) no intervention unless symptoms occur
- (B) prophylactic antibiotics
- (C) epidural corticosteroids
- (D) dye contrast study of the epidural space
- (E) neurosurgical exploration
A 33-year-old primigravid woman with myasthenia gravis, well-controlled with pyridostigmine, is in labor with the cervix dilated 7 cm. She has a headache and feels very nervous. Blood pressure is 160/115 mmHg, she has 3+ pitting edema, and urinalysis shows 4+ protein. Appropriate management of her labor should include
- (A) lumbar epidural block with bupivacaine 8 ml of 0.5% solution
- (B) chlorpromazine 2.5 mg administered intravenously
- (C) avoidance of narcotics
- (D) lumbar epidural block with 2-chloroprocaine 8 ml of 3% solution
- (E) chlorpromazine 10 mg administered intramuscularly
During therapy for eclampsia, toxic blood levels of magnesium sulfate can be distinguished from therapeutic levels by the presence of
- (A) diminished knee jerk reflex
- (B) a widened QRS complex on EKG
- (C) fetal tachycardia
- (D) maternal drowsiness
- (E) uterine rigidity
Which of the following is an effect of ritodrine?
- (A) Anisocoria
- (B) Hypocalcemia
- (C) Hypoglycemia
- (D) Hypokalemia
- (E) Urinary retention
During the first stage of labor, the pain of uterine contractions and cervical dilatation is transmitted via the spinal cord segments
- (A) T6 to L1
- (B) T6 to S5
- (C) T10 to L1
- (D) T10 to S1
- (E) T10 to S5
Normal pregnancy is associated with a decrease in each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) expiratory reserve volume
- (B) FEV1/FVC ratio
- (C) functional residual capacity
- (D) thoracic compliance
- (E) vital capacity
A complication of terbutaline therapy to terminate premature labor is
- (A) bronchoconstriction
- (B) hypoglycemia
- (C) fetal bradycardia
- (D) closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus
- (E) pulmonary edema
Which of the following is the most likely effect of administration of magnesium sulfate in a patient with preeclampsia?
- (A) Decreased motor end-plate sensitivity to acetylcholine
- (B) Decreased uteroplacental blood flow
- (C) Increased platelet aggregation
- (D) Increased systemic vascular resistance
- (E) Inhibited acetylcholinesterase