136 questions match your search.
A 31-year-old man received an uneventful epidural anesthetic for arthroscopy of the knee and meniscectomy. Twenty-four hours later he still has painless flaccid paralysis in both legs. This clinical presentation is most consistent with
- (A) adhesive arachnoiditis
- (B) anterior spinal artery thrombosis
- (C) epidural abscess
- (D) epidural hematoma
- (E) transverse myelitis
A 40-year-old woman has continuous nondermatomal burning pain of the distal foot four weeks after sustaining a metatarsal fracture. On examination, the foot is mildly swollen, tender, and cool. Which of the following statements concerning this condition is true?
- (A) A radiograph of the distal bones of the painful foot will show severe osteoporosis
- (B) A technetium scan of the distal joints of the painful foot will show decreased uptake
- (C) Early use of opioid analgesia will prevent progression of the symptoms
- (D) Intravenous phentolamine will relieve the pain
- (E) The chance of spontaneous recovery within eight weeks is greater than 80%
A patient undergoes differential spinal block for evaluation of persistent foot pain. If the pain returns coincident with a decrease in skin temperature, which of the following is the most appropriate conclusion?
- (A) A somatic origin is ruled out
- (B) The patient has causalgia
- (C) The patient has peripheral vascular disease
- (D) The pain is caused by central neuropathy
- (E) Lumbar sympathetic blocks are indicated
Compared with epidural administration of hydrophilic opioids, epidural administration of lipophilic opioids is associated with
- (A) earlier onset of pruritus
- (B) greater motor block when combined with local anesthetics
- (C) higher incidence of delayed respiratory depression
- (D) lesser sensitivity to reversal of analgesia by naloxone
- (E) slower onset of analgesia
Which of the following complications of caudal anesthesia with 0.25% bupivacaine is more likely in children than in adults?
- (A) Intravascular injection
- (B) Neurotoxicity
- (C) Profound motor block
- (D) Systemic toxicity
- (E) Total spinal block
A 65-kg man is scheduled for wrist surgery with intravenous regional anesthesia with 0.5% lidocaine 50 ml. Which of the following statements is true?
- (A) This anesthetic is contraindicated if the patient has sickle cell disease
- (B) Mottling of the skin after injection dictates abandonment of the technique
- (C) Tourniquet discomfort is an indication to inject more local anesthetic
- (D) Bupivacaine 0.5% could be substituted to prolong anesthesia
- (E) Epinephrine (1:400,000) should be added to prolong anesthesia
Which of the following statements concerning the use of epidural anesthesia for extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is true?
- (A) Adequate anesthesia can be obtained with fentanyl alone
- (B) Anesthesia decreases the incidence of hypothermia
- (C) Anesthesia decreases the incidence of ventricular dysrhythmias
- (D) Anesthesia is unnecessary in paraplegics with absence of sensation below T4
- (E) "Loss of resistance" should be performed with fluids rather than air
A 70-year-old man with stable angina is scheduled for cataract removal with a retrobulbar block. After injection of 5 ml of 0.75% bupivacaine, heart rate decreases from 90 to 55 bpm, and frequent premature ventricular contractions are noted on the EKG. These changes are most likely caused by
- (A) intravascular injection of bupivacaine
- (B) subarachnoid injection of bupivacaine
- (C) myocardial ischemia
- (D) oculocardiac reflex
- (E) retrobulbar hemorrhage
Which of the following statements regarding innervation of the upper extremity is true?
- (A) Blockade of the radial nerve decreases the patient's ability to spread the fingers apart
- (B) The brachial plexus receives preganglionic sympathetic fibers arising from C5 through T2
- (C) Interscalene injection of the brachial plexus at C6 is likely to spare the axillary nerve.
- (D) The musculocutaneous nerves receive contributions from C5 and C6
- (E) The vertebral artery lies posterior to the nerve roots of the brachial plexus
A 64-year-old patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease sustained fractures of ribs 4 through 8 on the left one hour ago. Examination shows agitation, heart rate of 120 bpm, respiratory rate of 30/min, and blood pressure of 180/100 mmHg. PaO2 is 70 mmHg and PaCO2 is 35 mmHg on room air. Radiographs of the chest show no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate immediate management?
- (A) Continuous epidural analgesia using local anesthetics
- (B) Mechanical ventilation
- (C) Infusion of midazolam
- (D) Patient-controlled analgesia with morphine sulfate
- (E) Surgical stabilization of rib fractures
A 75-year-old man in the PACU complains of severe pain following thoracotomy. Respiratory rate is 30/min; arterial blood gas values are PaO2 70 mmHg, PaCO2 56 mmHg, and pH 7.28 at an FiO2 of 0.6. The patient has a thoracic epidural catheter and received epidural morphine 2 mg 45 minutes earlier. Which of the following is the most appropriate immediate management?
- (A) Intravenous administration of naloxone
- (B) Epidural administration of additional morphine
- (C) Epidural administration of 0.125% bupivacaine
- (D) Epidural administration of fentanyl
- (E) Intubation of the trachea
During axillary brachial plexus anesthesia, motor block frequently precedes sensory block because of
- (A) conduction velocity of motor fibers
- (B) myelination of motor fibers
- (C) size of motor fibers
- (D) presence of septa between motor fibers
- (E) peripheral location of motor fibers in the nerve bundle
Which of the following is the most likely sequela of interscalene brachial plexus block?
- (A) Cervical epidural block
- (B) Hemidiaphragmatic paralysis
- (C) Pneumothorax
- (D) Seizure
- (E) Vocal cord paralysis
In a patient receiving an epidural analgesic infusion postoperatively, clear fluid is noted to drip back freely from the epidural catheter. Each of the following findings correctly identifies the associated fluid EXCEPT
- (A) precipitation when mixed with an equal volume of thiopental — local anesthetic
- (B) pH 7.1— saline solution
- (C) glucose 55 mg/dl - CSF
- (D) sodium 150 mEq/L - CSF
- (E) PCO2 51 mmHg - CSF
Retrobulbar block for ophthalmologic surgery can be administered safely to patients with which of the following conditions?
- (A) Agitation
- (B) Bleeding disorder
- (C) Frequent coughing spasms
- (D) Increased intraocular pressure
- (E) Perforated globe
Which of the following factors is the LEAST important determinant of postdural puncture headache?
- (A) Age of the patient
- (B) Gauge of the spinal needle
- (C) Gender of the patient
- (D) Pregnancy
- (E) Time until ambulation
Epidural administration of corticosteroids is most effective in relieving pain in patients with which of the following conditions?
- (A) Back pain caused by metastatic cancer
- (B) Postherpetic neuralgia
- (C) Postlaminectomy syndrome
- (D) Postural low back pain
- (E) Radiculopathy following disk herniation
Myofascial pain is an example of
- (A) a central pain state
- (B) neuropathic pain
- (C) psychogenic pain
- (D) somatic pain
- (E) visceral pain
Intractable pain due to unresectable pancreatic carcinoma is most effectively treated with
- (A) bilateral neurolytic intercostal blocks at T10-12
- (B) bilateral sympathetic blocks with phenol
- (C) celiac plexus block with alcohol
- (D) epidural block with phenol
- (E) subarachnoid block with alcohol
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation is LEAST likely to be effective in which of the following pain syndromes?
- (A) Acute postoperative pain
- (B) Chronic pancreatitis
- (C) Myofascial syndrome
- (D) Phantom limb pain
- (E) Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
Which of the following statements concerning use of amitriptyline to treat chronic pain is true?
- (A) It acts primarily via opioid receptors
- (B) It increases serotonin levels in the brain
- (C) It is rarely effective for postherpetic neuralgia
- (D) Onset of action occurs after four to six weeks of treatment
- (E) Response depends on reversal of depression
A 65-year-old woman has respiratory distress and loss of consciousness immediately following superficial and deep cervical plexus block for right carotid endarterectomy. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Phrenic nerve paralysis
- (B) Pneumothorax
- (C) Recurrent laryngeal nerve block
- (D) Subarachnoid injection
- (E) Vertebral artery injection
Which of the following statements concerning caudal anesthesia in children is true?
- (A) The dural sac extends further caudad than in adults
- (B) Delay of postoperative micturition occurs in most patients
- (C) The sensory level of analgesia is poorly correlated with the dose of local anesthetic
- (D) It is technically difficult because of poorly defined sacral anatomy
- (E) It is contraindicated in infants younger than 1 year of age
The physiologic function most likely to be spared when a local anesthetic differential nerve block is administered is
- (A) sweating
- (B) temperature sensation
- (C) proprioception
- (D) touch sensation
- (E) pain sensation
An otherwise healthy 42-year-old woman is referred for management of pain associated with adenocarcinoma of the breast and metastasis to the anterior body of L3. She perceives the pain as moderate and currently takes no pain medication. Her oncologist estimates her life expectancy to be 18 months. The most appropriate initial management is
- (A) a benzodiazepine as needed and at bedtime
- (B) an oxycodone preparation as needed and a tricyclic antidepressant at bedtime
- (C) intravenous patient-controlled analgesia
- (D) morphine infusion via an implanted epidural catheter
- (E) parenteral meperidine
An 8-kg, 1-year-old boy is scheduled for a bilateral inguinal hernia repair. If regional anesthesia is to be used for post-operative analgesia, which of the following statements is true?
- (A) Caudal administration of 0.25% bupivacaine will provide analgesia without evidence of motor block
- (B) Caudal administration of 0.125% bupivacaine is as effective as caudal administration of 0.25% bupivacaine
- (C) Caudal analgesia is more difficult to achieve in young children than in adults
- (D) The recommended volume of local anesthetic used for caudal analgesia in children is 3 ml per year of age
- (E) The volume of 0.25% bupivacaine required for bilateral ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerve blocks would be too large
Which of the following additives accelerates the onset of lidocaine axillary block without shortening duration?
- (A) Carbon dioxide
- (B) Dextran
- (C) Dextrose
- (D) Epinephrine
- (E) Hyaluronidase
Diplopia following lumbar puncture with a 25-gauge, 3 1/2-inch needle is the result of
- (A) stretching the abducens nerve
- (B) pressure on the optic nerve
- (C) distortion of the oculomotor nucleus from collapse of the wall of the third ventricle
- (D) the severity of the accompanying headache
- (E) compensatory cerebral swelling
A patient with lumbar disk disease requires lumbar epidural injection of a corticosteroid for control of low back pain. Which of the following statements concerning this treatment is true?
- (A) Maximum effect occurs one hour after injection
- (B) Maximum effect occurs when drug concentration peaks in cerebrospinal fluid
- (C) Maximum effect occurs during the acute phase of the disease
- (D) The beneficial effect results primarily from sympathetic neurolysis
- (E) It is contraindicated if the patient has had prior surgical procedures on the lumbar disks
Coughing that occurs during awake intubation is prevented by local anesthetic block of which of the following nerves?
- (A) Glossopharyngeal
- (B) Hypoglossal
- (C) Recurrent laryngeal and glossopharyngeal
- (D) Recurrent laryngeal and superior laryngeal
- (E) Superior laryngeal and glossopharyngeal
Block of the superficial cervical plexus is performed at which location?
- (A) At the midposterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
- (B) In the interscalene groove
- (C) Over the mastoid process
- (D) Over the transverse process of C4
- (E) Over Chassaignac's tubercle
After brachial plexus block, a patient has sensation over the inner aspect of the upper arm. Block of which of the following nerves would obtund this sensation?
- (A) Intercostobrachial
- (B) Median
- (C) Musculocutaneous
- (D) Radial
- (E) Ulnar
Two months ago a 68-year-old man with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus had a transurethral resection of the prostate under spinal anesthesia with tetracaine plus epinephrine. He now has numbness and tingling in both feet and disturbance of gait. Physical examination demonstrates stocking-type hypesthesia of both feet and ankles. The most likely diagnosis is
- (A) anterior spinal artery syndrome
- (B) diabetic neuropathy
- (C) adhesive arachnoiditis
- (D) cauda equina syndrome
- (E) peripheral nerve injury from the lithotomy position
The muscular action most likely to remain intact following an axillary brachial plexus block is
- (A) flexion at the elbow
- (B) extension at the wrist
- (C) flexion of digits 3, 4, and 5
- (D) extension of digits 1, 2, and 3
- (E) extension at the elbow
Surgery is cancelled 10 minutes after initiation of intravenous regional anesthesia with 50 ml of lidocaine 0.5%. To terminate anesthesia safely, what is the most appropriate timing for deflating the tourniquet?
- (A) Immediately if benzodiazepines have been administered
- (B) Immediately after intravenous administration of ephedrine 10 mg
- (C) Immediately, followed by repeated reinflation and deflation
- (D) In no less than 20 minutes after initial injection
- (E) In no less than 45 minutes after initial injection
A patient undergoes axillary block for placement of an arteriovenous shunt in the forearm. Blockade of the musculocutaneous nerve is not achieved. Injection of a local anesthetic at which of the following sites will provide the required sensory block?
- (A) Between the tendon of the palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis
- (B) Body of coracpbrachialis muscle
- (C) Medial to the brachial artery at the elbow
- (D) Proximal to the medial epicondyle against the medial surface of the humerus
- (E) Superficial to the pulse of the axillary artery
Following axillary block for insertion of an arteriovenous fistula in the forearm, a patient has pain on surgical incision. Which of the following nerves should be blocked to relieve this pain?
- (A) Axillary
- (B) Median
- (C) Musculocutaneous
- (D) Radial
- (E) Ulnar
When performed with identical doses, which of the following types of regional block is associated with the highest plasma concentration of the drug?
- (A) Brachial plexus
- (B) Caudal
- (C) Intercostal
- (D) Subcutaneous infiltration
- (E) Thoracic epidural
A 75-year-old man received an uneventful epidural anesthetic for total knee arthroplasty. Twenty-four hours later he has a painless flaccid paralysis in both legs. This clinical presentation is most consistent with
- (A) adhesive arachnoiditis
- (B) anterior spinal artery thrombosis
- (C) epidural abscess
- (D) epidural hematoma
- (E) transverse myelitis
An 18-year-old woman has knee pain during arthroscopy performed with femoral and sciatic nerve blocks for repair of a torn medial meniscus. The most appropriate management is addition of which of the following nerve blocks?
- (A) Deep peroneal
- (B) Obturator
- (C) Popliteal
- (D) Saphenous
- (E) Superficial peroneal
To eliminate involuntary expulsive effort with contraction in the second stage of labor, a nerve block must include at least
- (A) T6-T12
- (B) T4-S5
- (C) T8-L2
- (D) L1-S2
- (E) S2-S4
Which of the following is characteristic of low back pain associated with myofascial pain syndrome but not of pain associated with a herniated lumbar disk?
- (A) Loss of reflexes in the lower extremities
- (B) Pain along the distribution of nerve roots
- (C) Responsiveness to epidural corticosteroids
- (D) Sensitivity to injection at trigger points
- (E) Trophic alteration in the sympathetic nervous system
A 40-year-old man who is scheduled to undergo repair of a tendon laceration of the left hand has complete anesthesia in the median, radial, and ulnar nerve distributions after supraclavicular block. Two hours of tourniquet inflation are required for completion of the procedure. The most appropriate next step is an additional block of which of the following?
- (A) Axillary nerve
- (B) Intercostobrachial nerve
- (C) Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve
- (D) Musculocutaneous nerve
- (E) Stellate ganglion
Compared with epidural morphine, intrathecal morphine produces
- (A) better relief of visceral pain
- (B) greater loss of analgesia after administration of naloxone
- (C) less pruritus
- (D) less urinary retention
- (E) more respiratory depression
Following a vaginal hysterectomy in the lithotomy position under general anesthesia, a patient has numbness of the lateral aspect of the left calf and medial half of the dorsum of the left foot. On physical examination she has footdrop and the toes cannot be extended. Which nerve is most likely to be involved?
- (A) Common peroneal nerve
- (B) Deep peroneal nerve
- (C) Posterior tibial nerve
- (D) Saphenous nerve
- (E) Sciatic nerve
A celiac plexus block provides effective relief of pain associated with primary cancers at each of the following locations EXCEPT the
- (A) adrenal gland
- (B) liver
- (C) pancreas
- (D) sigmoid colon
- (E) stomach
Each of the following is a complication or side effect of neurolytic celiac plexus blockade EXCEPT
- (A) constipation
- (B) hematuria
- (C) orthostatic hypotension
- (D) paraplegia
- (E) pneumothorax
In performing a diagnostic left lumbar sympathetic block for lower extremity claudication, the tip of the needle ideally should lie at point
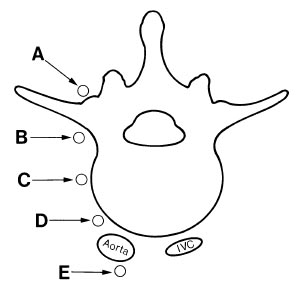
- (A) A
- (B) B
- (C) C
- (D) D
- (E) E
Five minutes after intrathecal administration of tetracaine 12 mg in hyperbaric solution, a 60-year-old man has a weak hand grasp. Respirations are normal, heart rate has decreased from 80 to 45 bpm, and blood pressure has decreased from 150/80 to 90/50 mmHg. The most appropriate management at this time is
- (A) administration of atropine
- (B) administration of ephedrine
- (C) administration of phenylephrine
- (D) placement of the patient in the head-down position
- (E) observation
A patient is scheduled for amputation of the third metatarsal. A tourniquet will not be used during the procedure. The most effective anesthesia will be provided by block of which of the following nerves?
- (A) Femoral
- (B) Common peroneal and tibial
- (C) Sural and deep peroneal
- (D) Sural and tibial
- (E) Tibial, saphenous, and deep peroneal
Compared with adults, caudal anesthesia in children is associated with
- (A) higher risk for subarachnoid puncture
- (B) more severe hypotension
- (C) more rapid onset of sensory block
- (D) smaller volume of anesthetic per kilogram of body weight
- (E) toxic effects at lower serum levels of bupivacaine
Forty-eight hours after thoracotomy, a patient's T6-7 epidural catheter is removed and the distal 2 cm is noted to be missing. The patient felt no pain during removal and neurologic examination shows no abnormalities. After informing the patient, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- (A) Observation
- (B) Culture of cerebrospinal fluid
- (C) MRI of the thoracic spine
- (D) Myelography
- (E) Surgical removal of the catheter
Which of the following statements concerning interscalene brachial plexus block is true?
- (A) The three trunks of the plexus are in the same fascial plane as the internal jugular vein
- (B) Distal spread of anesthetic past the humeral head is accelerated by adduction of the arm
- (C) Anesthetic solution can spread up the fascial sheaths to involve the stellate ganglion
- (D) Ipsilateral diaphragmatic paralysis results from epidural spread
- (E) Rich vascularity in the sheaths promotes rapid vascular uptake of anesthetic
Each of the following is a complication of celiac plexus block with 0.5% lidocaine 40 ml EXCEPT
- (A) hematuria
- (B) ileus
- (C) postural hypotension
- (D) retroperitoneal hematoma
- (E) weakness of hip flexors
A patient who has severe pain from unresectable cancer of the base of the tongue is referred for a neurolytic block. A block of which of the following will be effective?
- (A) Gasserian ganglion
- (B) Glossopharyngeal nerve
- (C) Hypoglossal nerve
- (D) Mandibular nerve
- (E) Vagus nerve
A 28-year-old woman receives a lumbar epidural anesthetic for uncomplicated labor and delivery. During removal of the catheter, 1 cm breaks off and remains in her back. After informing the patient, the most appropriate management is
- (A) no intervention unless symptoms occur
- (B) prophylactic antibiotics
- (C) epidural corticosteroids
- (D) dye contrast study of the epidural space
- (E) neurosurgical exploration
After receiving an axillary block for carpal tunnel release, a patient has pain on incision. Which of the following nerves should be blocked at the level of the elbow to relieve the pain?
- (A) Intercostobrachial
- (B) Median
- (C) Musculocutaneous
- (D) Radial
- (E) Ulnar
A 54-year-old man receives 25 ml of a 50% alcohol and 0.25% bupivacaine solution for celiac plexus block. During the next 20 minutes, blood pressure decreases from 130/75 mmHg to 85/55 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Intravascular injection
- (B) Retroperitoneal hemorrhage
- (C) Splanchnic vasodilation
- (D) Subarachnoid blockade
- (E) Tension pneumothorax
Prompt control of seizures induced by bupivacaine is necessary because
- (A) cerebral metabolic rate for oxygen increases more than cerebral blood flow
- (B) cerebral blood flow is increased
- (C) bupivacaine decreases aerobic cerebral metabolism
- (D) cardiac failure may occur
- (E) ventilation may be impaired
Each of the following is a complication of stellate ganglion block EXCEPT
- (A) brachial plexus block
- (B) diplopia
- (C) local anesthetic-induced seizure
- (D) recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy
- (E) subarachnoid block
A patient receives 1.5% bupivacaine 40 ml and epinephrine 1:200,000 for axillary brachial plexus block for reduction of a forearm fracture. The tourniquet is inflated to 300 mmHg; 45 minutes later, the patient has pain that radiates to the posteromedial elbow. Which of the following nerves is NOT adequately blocked?
- (A) Intercostobrachial
- (B) Median
- (C) Musculocutaneous
- (D) Ulnar
- (E) Radial
Which of the following nerves is most likely to be injured by a fracture of the shaft of the humerus?
- (A) Axillary
- (B) Median
- (C) Musculocutaneous
- (D) Radial
- (E) Ulnar
Following completion of an ankle block, the patient reports intact sensation on the tips of the toes. Which of the following nerves was blocked inadequately?
- (A) Deep peroneal
- (B) Posterior tibial
- (C) Saphenous
- (D) Superficial peroneal
- (E) Sural
A patient has seizure activity 30 seconds after injection of 0.25% bupivacaine 2 ml with epinephrine 1:200,000 for stellate ganglion block. The most likely cause is
- (A) reaction to epinephrine in the anesthetic solution
- (B) anaphylactoid reaction to bupivacaine
- (C) subarachnoid injection of bupivacaine
- (D) peridural venous injection of bupivacaine
- (E) vertebral artery injection of bupivacaine
Mepivacaine 40 ml of a 1% solution with epinephrine 1:200,000 is injected into the brachial plexus sheath at the axilla after eliciting a paresthesia in the ulnar nerve distribution. Which of the following is most likely to remain intact?
- (A) Adduction of the thumb
- (B) Flexion at the wrist
- (C) Sensation of the lateral forearm
- (D) Sensation on the palmar surface of the lateral three and one half fingers
- (E) Sensation on the palmar surface of the medial one and one half fingers
A 30-year-old primiparous woman delivered a healthy infant by cesarean section during uneventful spinal anesthesia with tetracaine 10 mg in 2 ml of 5% dextrose solution. Twelve hours after delivery she has bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensibility, but not touch, below T8 and paralysis of both legs. The most likely cause of this complication is
- (A) chemical arachnoiditis
- (B) injection of tetracaine into the spinal cord
- (C) demyelination of the posterior tracts
- (D) thrombosis of the anterior spinal artery
- (E) cord transection from spondylolisthesis
Which of the following is a cardiorespiratory effect of epidural block to a T4 sensory level?
- (A) Decreased expiratory reserve volume
- (B) Decreased tidal volume
- (C) Increased circulating catecholamine concentrations
- (D) Increased heart rate
- (E) Unchanged vital capacity
One day after a vaginal hysterectomy under epidural anesthesia, a patient has numbness and inability to dorsiflex the right foot. Her legs were placed in leg holders during the operation. The most likely cause is
- (A) epidural hematoma
- (B) common peroneal nerve injury
- (C) sacral nerve root injury
- (D) sacral plexus injury
- (E) sciatic nerve injury
Each of the following landmarks is used in performing wrist block to remove a cystic mass on the fourth digit EXCEPT the
- (A) extensor pollicis longus tendon
- (B) ulnar artery
- (C) palmaris longus tendon
- (D) flexor carpi radialis tendon
- (E) flexor carpi ulnaris tendon
In an Infant, spinal anesthesia to a sensory level of T8 is achieved with tetracaine administered at the L2-3 interspace. Compared with spinal anesthesia to the same sensory level in an adult, this anesthetic is associated with a
- (A) higher risk for neurotoxicity
- (B) higher risk for systemic toxicity
- (C) lower risk for spinal cord injury
- (D) more significant decrease in blood pressure
- (E) shorter duration of action
A patient has pain in the left thoracic wall associated with metastatic rib lesions. An intrathecal neurolytic block with 6% phenol in glycerin is planned for pain relief. Prior to performing the block, the patient should be placed in which of the following positions?
- (A) Left lateral semisupine
- (B) Right lateral semisupine
- (C) Left lateral semiprone
- (D) Right lateral semiprone
- (E) Prone
A 35-year-old man has acute onset of low back pain, lower extremity weakness, and bladder dysfunction. He had a lumbar laminectomy two years ago. A myelogram shows disk herniation at L4-5. The most appropriate management is
- (A) bed rest
- (B) administration of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent
- (C) epidural administration of a corticosteroid
- (D) epidural administration of a local anesthetic
- (E) surgical decompression
During surgery of the forearm under axillary block, a patient has pain in the lateral aspect of the forearm and responds by flexing the elbow. The most likely cause is inadequate block of which of the following nerves?
- (A) Axillary
- (B) Intercostobrachial
- (C) Musculocutaneous
- (D) Radial
- (E) Ulnar
Which of the following findings best indicates complete resolution of spinal anesthesia?
- (A) Ability to ambulate
- (B) Ability to urinate
- (C) Perianal pinprick sensation
- (D) Pain at the surgical site
- (E) Proprioception of the big toe
A patient has hoarseness after undergoing surgery involving the aortic arch. The most likely cause is an injury to which of the following nerves?
- (A) Glossopharyngeal
- (B) Left recurrent laryngeal
- (C) Right recurrent laryngeal
- (D) Left superior laryngeal
- (E) Right superior laryngeal
A patient receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy for depression undergoes an emergency cholecystectomy. Which of the following is the best means of providing postoperative analgesia in this patient?
- (A) Epidural analgesia using 0.25% bupivacaine
- (B) Intravenous meperidine
- (C) Epidural analgesia using meperidine
- (D) Epidural analgesia using 1% lidocaine with epinephrine
- (E) Intercostal analgesia using 1% lidocaine with epinephrine
Which of the following statements concerning postherpetic neuralgia is true?
- (A) It is effectively treated with neurolytic surgery
- (B) It is effectively treated with sympathetic nerve blocks
- (C) Duration is three to four weeks
- (D) Hyperesthesia occurs in the affected area
- (E) It occurs predominantly in adolescents
A 70-kg, 50-year-old man is scheduled for muscle flap closure of a decubitus ulcer over the sacrum. He has been quadriplegic at the level of C6-7 for six years. Which of the following is most likely to result from subarachnoid anesthesia with tetracaine 10 mg for this procedure?
- (A) Atrioventricular block
- (B) Decreased risk for autonomic dysreflexia
- (C) Impaired expiratory muscle function
- (D) Impaired inspiratory muscle function
- (E) Inadequate block of spastic movements
Which of the following statements about patient-controlled analgesia using opioids is true?
- (A) It is not associated with respiratory depression
- (B) It obviates loading doses
- (C) It requires a background opioid infusion to be effective
- (D) It requires intravenous administration to be effective
- (E) It requires less drug than intramuscular dosing for similar analgesia
After termination of an inhalation anesthetic, patient-controlled analgesia will
- (A) be effective without a loading dose of opioid if started in the immediate postanesthetic period
- (B) be associated with greater analgesic requirements than conventional intramuscular opioid techniques
- (C) cause addiction or dependence to opioids if continued for more than 72 hours
- (D) produce less patient satisfaction than intermittent intravenous administration of opioids
- (E) show a diurnal variation in analgesic requirement
Six months after repair of a lacerated peroneal nerve, a patient has electric-shock-like pain when pressure is applied to the middle of the gastrocnemius muscle. The most appropriate initial management is
- (A) administration of carbamazepine
- (B) epidural injection of morphine
- (C) local infiltration with bupivacaine
- (D) lumbar sympathetic blockade
- (E) peroneal nerve blockade
With an interscalene brachial plexus block
- (A) more local anesthetic drug is required than for axillary block
- (B) the biceps and brachialis muscles are blocked last
- (C) the intercostobrachial nerve is usually blocked
- (D) the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve is usually spared
- (E) the ulnar nerve is most likely to be spared
A woman has weakness of the right quadriceps and a decreased knee jerk reflex on the right one day after forceps delivery under epidural anesthesia. The most likely cause is
- (A) epidural hematoma
- (B) intrapelvic nerve trauma
- (C) lithotomy positioning
- (D) reaction to the preservative in the anesthetic solution
- (E) trauma from the epidural needle
An axillary block is administered to a 60-kg patient using 40 ml of 0.5% bupivacaine. Ten minutes after placement of the block, the patient has a seizure. Which of the following statements is true?
- (A) A low serum albumin concentration could have contributed to the occurrence of the seizure
- (B) CNS hypoperfusion is the most likely cause of the seizure
- (C) The seizure was probably secondary to an allergic reaction to the local anesthetic
- (D) The use of an equipotent dose of lidocaine rather than bupivacaine would have decreased the likelihood of
- the seizure
Which of the following statements concerning postspinal headache is true?
- (A) Cerebrospinal fluid leukocytosis occurs
- (B) Intravenous caffeine therapy is more effective than epidural blood patch
- (C) The incidence decreases with age
- (D) The incidence is higher in males than in females of all ages
- (E) The incidence is the same after single or multiple dural punctures
After an axillary brachial plexus block, the patient feels pain when the surgeon clips the skin over the thenar eminence. The most likely cause is inadequate anesthesia in the distribution of the
- (A) intercostobrachial nerve
- (B) median nerve
- (C) musculocutaneous nerve
- (D) radial nerve
- (E) ulnar nerve
Properly performed local anesthetic block of the celiac plexus
- (A) requires that the needle tip be positioned anterior to the vertebral body of LI
- (B) preserves efferent parasympathetic outflow
- (C) produces urinary retention
- (D) is not associated with hypotension
- (E) produces truncal cutaneous hypesthesia
A 26-year-old woman comes to a pain clinic because of pain, swelling and limitation of motion in the right knee for six months following a blow to the knee. Findings on knee arthroscopy and leg roentgenograms are normal. The best trial of therapy is
- (A) right paravertebral lumbar sympathetic nerve block
- (B) epidural administration of a steroid
- (C) intrathecal administration of an opioid
- (D) tricyclic antidepressants for one month
- (E) a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug for five days
A 45-kg, 80-year-old woman undergoes pin fixation of the right hip in the lateral decubitus position under spinal anesthesia. One day after the operation, she cannot move her left ankle or foot actively. The most likely cause is
- (A) compression of the sciatic nerve
- (B) compression of the common peroneal nerve
- (C) injury of the nerve root at L4-5
- (D) stretching of the femoral nerve
- (E) stretching of the tibial nerve
Which of the following is associated with the application of a transdermal fentanyl patch?
- (A) Achievement of a peak plasma level within one hour
- (B) Continued uptake after patch removal
- (C) Dose-independent plasma clearance
- (D) Tachyphylaxis when used for cancer pain
- (E) Naloxone-resistant toxicity
A tourniquet with dual bladders is being used for intravenous regional anesthesia of the upper extremity. At what point in the procedure should the distal tourniquet be inflated?
- (A) During injection of the local anesthetic
- (B) After the patient complains of tourniquet pain
- (C) Coincident with inflation of the proximal tourniquet
- (D) After the proximal tourniquet is deflated
- (E) Prior to exsanguination of the limb
An obese, 75-year-old woman is scheduled for open reduction of a left forearm fracture. Thirty minutes after successful interscalene block using 20 ml of 2% lidocaine, she becomes dyspneic. The dyspnea is most likely related to
- (A) cervical epidural block
- (B) cervical sympathetic block with bronchospasm
- (C) chylothorax
- (D) elevation of the left hemidiaphragm
- (E) recurrent laryngeal nerve block
A successful celiac plexus block can be expected to
- (A) block parasympathetic fibers to the adrenal medulla
- (B) block sympathetic fibers to the sigmoid colon
- (C) block somatic fibers to the pancreas
- (D) enhance peristalsis
- (E) inhibit ejaculation
Which of the following procedures is most specific for diagnosing reflex sympathetic dystrophy in a patient with pain of the lower extremity?
- (A) Caudal epidural local anesthetic block
- (B) Differential spinal anesthesia
- (C) Intravenous regional administration of bretylium
- (D) Lumbar epidural administration of a corticosteroid
- (E) Paramedian L1-L5 facet injections of lidocaine
In an infant, spinal anesthesia to a sensory level of T8 is achieved with tetracaine administered at the L2-3 interspace. Compared with spinal anesthesia to the same sensory level in an adult, this anesthetic is associated with a
- (A) greater decrease in blood pressure
- (B) higher risk for neurotoxicity
- (C) higher risk for systemic toxicity
- (D) lower risk for spinal cord injury
- (E) shorter duration of action
Which of the following correctly describes the anatomic location of the stellate ganglion?
- (A) Anterior to the transverse process of C5
- (B) Anterior to the transverse process of C7
- (C) Posterior to the prevertebral fascia
- (D) Posterior to the vertebral artery
- (E) Lateral to the carotid artery
Which of the following statements concerning intercostal nerve block for postoperative pain is true?
- (A) Block at the midaxillary line provides analgesia for the anterior and lateral abdominal walls
- (B) Blood levels of local anesthetic are higher than after an axillary block
- (C) Intravascular injection is unlikely
- (D) Loss of resistance assures proper needle placement
- (E) Paravertebral spread is prevented by adding epinephrine to the local anesthetic solution
During open reduction of a tibial fracture, a tourniquet cuff is applied around the proximal thigh and inflated to 300 mmHg. Which of the following is most likely to prevent pain and hypertension caused by the tourniquet?
- (A) Intravenous administration of fentanyl during subarachnoid block
- (B) Lumbar sympathetic block
- (C) Spinal anesthesia to a T6 sensory level
- (D) Obturator nerve block
- (E) General anesthesia
Which of the following is the most likely cause of apnea occurring after a retrobulbar block?
- (A) Epidural injection
- (B) Increased intracranial pressure
- (C) Oculopontine reflex
- (D) Ophthalmic artery injection
- (E) Subarachnoid injection
If both recurrent laryngeal nerves were severed during a difficult thyroidectomy for cancer, the most likely finding would be
- {A) paralysis of the cricothyroid muscles
- (B) cadaveric positioning of the true vocal cords
- (C) anesthesia of both sides of the epiglottis
- (D) bilateral pure adductor vocal cord paralysis
- (E) stridor
Neurolytic block is most appropriate for
- (A) abdominal pain secondary to hepatic carcinoma
- (B) abdominal pain secondary to chronic pancreatitis
- (C) persistent chest wall pain secondary to intercostal neuralgia following a thoracotomy for trauma
- (D) reflex sympathetic dystrophy of the upper extremity with an excellent but transient response to a series of stellate ganglion blocks with local anesthetic
- (E) a diabetic patient scheduled for surgical sympathectomy to relieve unilateral lower extremity pain secondary to severe peripheral vascular disease
Block of each of the following nerves is required for inguinal herniorrhaphy EXCEPT the
- (A) genitofemoral
- (B) iliohypogastric
- (C) ilioinguinal
- (D) obturator
- (E) twelfth thoracic
A patient has a seizure within seconds after receiving a retrobulbar injection of 0.5% bupivacaine with epinephrine 1:200,000. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Air embolism
- (B) Oculocardiac reflex
- (C) Ophthalmic artery injection
- (D) Retrobulbar hemorrhage
- (E) Subdural injection
Which of the following statements concerning the use of epidural opioids during labor is true?
- (A) Fentanyl decreases the concentration of epidural bupivacaine required for satisfactory analgesia
- (B) Fentanyl is an effective analgesic for the second stage of labor
- (C) Sufentanil is an unsatisfactory analgesic for labor
- (D) The addition of epinephrine to morphine prolongs the duration of analgesia
- (E) The duration of analgesia with fentanyl is six to ten hours
Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacologic therapy for trigeminal neuralgia?
- (A) Buprenorphine
- (B) Carbamazepine
- (C) Chlorpromazine
- (D) Pentazocine
- (E) Phenelzine
Nine months after sustaining an injury to the left forearm, a 30-year-old woman has diffuse, burning pain on the anterior aspect of the forearm and posterior aspect of the hand and discoloration of the skin in the affected areas. The patient should be informed that
- (A) if left untreated, muscle atrophy may develop in the involved limb
- (B) if left untreated, the pain will remain well localized
- (C) physical therapy is not indicated
- (D) the symptoms are directly related to the severity of the initial injury
- (E) the symptoms are most likely secondary to underlying peripheral vascular disease
The plasma concentration of equal doses of a local anesthetic is highest when the site of administration is
- (A) axillary brachial plexus
- (B) caudal
- (C) intercostal
- (D) lumbar epidural
- (E) subcutaneous
The last muscle to be affected by an interscalene brachial plexus block is the
- (A) brachialis
- (B) brachioradialis
- (C) biceps
- (D) flexor carpi radialis
- (E) interosseous
Each of the following is a complication of celiac plexus block with 0.5% lidocaine 40 ml EXCEPT
- (A) hematuria
- (B) ileus
- (C) postural hypotension
- (D) retroperitoneal hematoma
- (E) weakness of hip flexors
A 30-year-old woman has difficulty talking 15 minutes after initiation of interscalene block for closed reduction of a dislocated shoulder. The most likely cause is
- (A) cervical sympathetic block
- (B) delayed systemic toxic reaction
- (C) phrenic nerve paralysis
- (D) pneumothorax
- (E) recurrent laryngeal nerve block
A successful ankle block for transmetatarsal amputation of the first and second toes should include each of the following nerves EXCEPT the
- (A) saphenous
- (B) deep peroneal
- (C) superficial peroneal
- (D) sural
- (E) tibial
A patient is placed in the prone jackknife position for lumbar subarachnoid injection of tetracaine 10 mg in 10 ml of preservative-free sterile water. Which of the following results is most likely?
- (A) Respiratory insufficiency
- (B) Sensory and motor block at T4-S1
- (C) Sensory and motor block at L1-S5
- (D) Sensory loss without motor block at L1-S5
- (E) Sensory and motor block at S3-S5
A 65-year-old man undergoes prostatectomy in the lithotomy position under spinal anesthesia using bupivacaine 12 mg. Ten hours later, he reports that his left foot is numb. Examination shows decreased pinprick sensation over the lateral dorsal aspect of the left foot; dorsiflexion is limited. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Cauda equina syndrome
- (B) Compression of the common peroneal nerve
- (C) Compression of the posterior tibial nerve
- (D) L5 nerve root damage
- (E) Stretching of the sciatic nerve
A 58-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis and hyperactive gag reflex requires awake intubation prior to cervical spine stabilization. Which of the following regional nerve blocks is most appropriate?
- (A) Deep cervical plexus
- (B) Glossopharyngeal nerve
- (C) Hypoglossal nerve
- (D) Superior laryngeal nerve
- (E) Trigeminal nerve
The condition LEAST likely to be associated with sustained pain relief following a nerve block is
- (A) causalgia
- (B) myofascial pain
- (C) diabetic neuropathy
- (D) acute herpes zoster
- (E) reflex sympathetic dystrophy
Bupivacaine 30 ml injected into the inguinal perivascular space will usually block the
- (A) femoral, lateral femoral cutaneous, and obturator nerves
- (B) ilioinguinal, femoral, and sciatic nerves
- (C) femoral, sciatic, and obturator nerves
- (D) ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric, and pudendal nerves
- (E) sciatic, femoral, and posterior femoral cutaneous nerves
In a patient with peripheral vascular disease, the most likely result of lumbar sympathetic block is
- (A) increased blood flow to skin and decreased blood flow to muscle
- (B) increased blood flow to skin and unchanged blood flow to muscle
- (C) increased blood flow to skin and muscle
- (D) decreased blood flow to skin and muscle
- (E) decreased blood flow to skin and unchanged blood flow to muscle
Immediately after a retrobulbar block for cataract surgery, the eye grossly protrudes and the patient has the sensation of pressure in the eye. The most appropriate initial intervention is
- (A) hyperventilation
- (B) surgical drainage of a hematoma
- (C) manual compression of the globe
- (D) administration of atropine intravenously
- (E) administration of mannitol intravenously
Which of the following treatments is LEAST effective in patients with acute herpes zoster?
- (A) Acyclovir
- (B) Antidepressants
- (C) Epidural block
- (D) Opioids
- (E) Sympathetic nerve block
Percutanous cordotomy is being considered for a patient with severe pain that has persisted for three months after amputation of the arm for osteogenic sarcoma. Which of the following statements is true?
- (A) An effective cordotomy will produce motor block
- (B) A series of stellate ganglion blocks will provide permanent relief
- (C) Cordotomy must be performed with the patient awake
- (D) Cordotomy will effectively relieve phantom limb pain
- (E) Spinal opioids are an alternative treatment of this pain
Which of the following will most closely mimic the effects of stellate ganglion block?
- (A) Axillary perivascular block with 25 mL of 1.5% lidocaine
- (B) Cervical nerve block at C2-5 with 2 mL of 1.5% lidocaine
- (C) Supraclavicular block at the level of the first rib with 25 mL of 1.5% lidocaine
- (D) Block of the median, radial, ulnar, musculocutaneous, and intercostobrachial nerves
- (E) Excision of thoracic sympathetic ganglia Tl-4
Which surface area of the upper extremity is most likely to be unanesthetized by an interscalene brachial plexus block?
- (A) Hypothenar eminence
- (B) Thenar eminence
- (C) Dorsolateral surface of the hand
- (D) Lateral aspect of the forearm
- (E) Lateral surface of the upper arm
Which of the following anesthetic techniques is most appropriate for a woman in the second stage of labor?
- (A) Epidural opioids
- (B) Local infiltration of the perineum
- (C) Lumbar sympathetic block
- (D) Paracervical nerve block
- (E) Pudendal nerve block
Each of the following is an effect of intravascular radiographic contrast media EXCEPT
- (A) altered protein binding of anesthetic drugs
- (B) bronchospasm
- (C) increased systemic vascular resistance
- (D) pulmonary edema
- (E) seizures
A 30-year-old man has had burning pain, allodynia, and edema of the hand for six weeks after sustaining a forearm fracture. Appropriate treatment includes each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) physical therapy, employing stress loading
- (B) oral prazosin
- (C) intravenous regional sympathetic block with guanethidine
- (D) stellate ganglion block with 6% phenol
- (E) transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
Which of the following is most indicative of reflex sympathetic dystrophy?
- (A) Dry skin
- (B) Dull pain that improves with movement
- (C) Fasciculations
- (D) Motor weakness
- (E) Pallor and cyanosis
Block of each of the following nerves is required for inguinal herniorrhaphy EXCEPT the
- (A) genitofemoral
- (B) iliohypogastric
- (C) ilioinguinal
- (D) obturator
- (E) twelfth thoracic
Five minutes after a stellate ganglion block is performed, a patient becomes restless, then apneic. The most likely cause is
- (A) paratracheal hematoma
- (B) phrenic nerve block
- (C) recurrent laryngeal nerve block
- (D) subarachnoid injection
- (E) vertebral artery injection
During postoperative indirect laryngoscopy, the vocal cords appear symmetric during quiet breathing and approximate to the left of midline during phonation. The most likely cause is
- (A) pure abductor paralysis of the left cord
- (B) pure abductor paralysis of the right cord
- (C) abductor and adductor paralysis of the left cord
- (D) abductor and adductor paralysis of the right cord
- (E) adductor paralysis of both cords
Neurolytic block is most appropriate for
- (A) abdominal pain secondary to hepatic carcinoma
- (B) abdominal pain secondary to chronic pancreatitis
- (C) persistent chest wall pain secondary to intercostal neuralgia following a thoracotomy for trauma
- (D) reflex sympathetic dystrophy of the upper extremity with an excellent but transient response to a series of stellate ganglion blocks with local anesthetic
- (E) a diabetic patient scheduled for surgical sympathectomy to relieve unilateral lower extremity pain secondary
Twenty minutes after an axillary block, the patient reports feeling over the "back of the hand." Examination shows normal sensation over the lateral aspect of the dorsum of the hand and the dorsal base of the thumb and index finger. Supplementary anesthesia of this area can be provided by blocking which of the following nerves?
- (A) Ulnar
- (B) Musculocutaneous
- (C) Median
- (D) Radial
- (E) Intercostobrachial
In patients with reflex sympathetic dystrophy affecting the arm, which of the following findings indicates a therapeutic block?
- (A) Bradycardia
- (B) Contralateral nasal congestion
- (C) Hoarseness
- (D) Increased skin temperature
- (E) Ipsilateral Horner's syndrome
The most likely effect of a celiac plexus block for an abdominal operation is
- (A) bowel distention
- (B) hypotension
- (C) incisional analgesia
- (D) muscle relaxation
- (E) urinary retention
A patient receives remifentanil 25 mcg just before retrobulbar block with 0.25% bupivacaine 4 mL. Over the next 10 minutes, he develops apnea and loses consciousness. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
- (A) Effects of remifentanil
- (B) Injection of local anesthetic into cerebrospinal fluid
- (C) Intravascular injection of local anesthetic
- (D) Oculocardiac reflex
- (E) Systemic absorption of local anesthetic
The condition LEAST likely to be associated with sustained pain relief following a nerve block is
- (A) causalgia
- (B) myofascial pain
- (C) diabetic neuropathy
- (D) acute herpes zoster
- (E) reflex sympathetic dystrophy
During axillary block of the brachial plexus, which nerve is most likely to be encountered if the needle is inserted through the posterior wall of the artery?
- (A) Intercostobrachial
- (B) Median
- (C) Musculocutaneous
- (D) Radial
- (E) Ulnar