10 Random Questions
Which of the following is most likely to occur during deliberate hypotension with trimethaphan?
- (A) Bronchoconstriction
- (B) Cerebral vasodilation
- (C) Increased heart rate
- (D) Potentiation of pancuronium
- (E) Pupillary constriction
Which of the following findings necessitates the preoperative insertion of a ventricular pacemaker in a 48-year-old man scheduled to undergo cholecystectomy?
- (A) Atrial flutter with 3:1 atrioventricular block
- (B) Bifascicular (right bundle branch block and left anterior hemiblock) block
- (C) Left bundle branch block with first-degree atrioventricular block
- (D) Second-degree (Mobitz I) atrioventricular block
- (E) Second-degree (Mobitz II) atrioventricular block
A healthy 57-year-old man with a ureteral calculus is scheduled for immersion extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Which of the following statements is true?
- (A) Delivery of the shock wave is timed by the R wave of the ECG
- (B) Continuous epidural anesthesia is contraindicated because of the risk for infection
- (C) If a regional technique is used, a T10 sensory level is required for adequate anesthesia
- (D) If general anesthesia is used, high tidal volumes and low respiratory rate are preferred
- (E) Removal of the patient from the bath is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure
Prolonged respiratory depression following administration of morphine is more likely in patients with chronic renal faillure than in patients with normal kidney function because of
- (A) decreased biotransformation
- (B) decreased protein binding
- (C) decreased volume of distribution
- (D) delayed excretion of morphine metabolites
- (E) the effect of acidosis on morphine ionization
A 70-kg 24-year-old man with bilateral pneumonia whose lungs are being mechanically ventilated has the following measured parameters: tidal volume 750 ml; FiO2 0.7; rate 12/min; positive end-expiratory pressure 10 cmH2O; PaO2 75 mmHg; PaCO2 55 mmHg; pH 7.30. Which of the following alterations should be made in the ventilatory settings?
- (A) Decreasing positive end-expiratory pressure
- (B) Decreasing respiratory rate
- (C) Increasing fresh gas flow rate
- (D) Increasing FiO2
- (E) Increasing tidal volume
Which of the following is the most likely cause of the rapid onset of local anesthesia when sodium bicarbonate is added to lidocaine?
- (A) Decreased extracellular calcium ion concentration
- (B) Increased extracellular pH
- (C) Increased intracellular pH
- (D) Increased ionized lidocaine diffusion
- (E) Increased nonionized lidocaine concentration
Pulse oximetry accurately reflects SaO2 in which of the following situations?
- (A) Administration of indocyanine green
- (B) Administration of methylene blue
- (C) Carboxyhemoglobinemia
- (D) 40% fetal hemoglobin concentration
- (E) Methemoglobinemia
A normal adult is receiving general anesthesia via a standard circle system and controlled ventilation. Mass spectrometer data are shown. Which event is most compatible with these data?
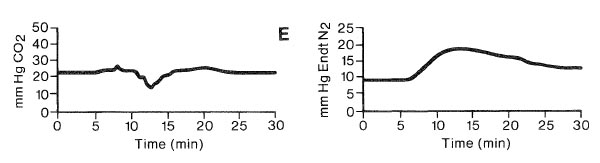
- (A) Endobronchial intubation
- (B) Hemorrhagic shock
- (C) Incompetent expiratory valve
- (D) Substantial decrease in fresh gas flow
- (E) Venous air embolism
Maternal hyperventilation to a PaCO2 of 20 mmHg during labor can result in
- (A) decreased fetal trapping of local anesthetics
- (B) fetal metabolic acidosis
- (C) fetal respiratory acidosis
- (D) increased oxygen release at the placenta
- (E) uterine vasodilation
A full-term neonate has physical findings suggestive of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Initial Apgar score is 2. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management?
- (A) Placement of an orogastric tube
- (B) Insertion of a chest tube
- (C) Controlled ventilation by face mask
- (D) Controlled ventilation through an endotracheal tube
- (E) Spontaneous ventilation through an endotracheal tube